For the description of the property element see section 9.3 on page
![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) .
.





Introduction: 0011
For the description of the property element see section 9.3 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) .
.
The property vector type is determined by a natural number, which immediately follows after the introduction. In the list of the valid domains the possible properties are listed (see section 9.14.2 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) , table 2 on page
, table 2 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) and table 5 on page
and table 5 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) ). The number for the property (vector) type is the number of the property in the valid domains list. Counted are only property domains and the count starts with 0 .
). The number for the property (vector) type is the number of the property in the valid domains list. Counted are only property domains and the count starts with 0 .
In the valid domain list first domains for values (see section 9.14.2 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) )
and than the domains for elements (see section 9.14.2 on page
)
and than the domains for elements (see section 9.14.2 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) are listed.
Inherited property domains, which are not overwritten, will be counted as if they are behind the domains of the current (respectively next) root-element. (The closer the inherited root-element is to the inheriting root-element, the smaller are the numbers of inherited property domains [respectively for values and element domains].)
are listed.
Inherited property domains, which are not overwritten, will be counted as if they are behind the domains of the current (respectively next) root-element. (The closer the inherited root-element is to the inheriting root-element, the smaller are the numbers of inherited property domains [respectively for values and element domains].)
For property types, that exists in the Fib object, but for which no domain exists, a domain (e.g. the standard domain) must inserted in the domains for values. Only then the property vector types can be numbered.
The number of bits, that are needed for the number of property vector type, results from the number of defined (including inherited) property domains 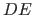 as a whole, it is
as a whole, it is
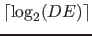 .
If for example property domains
.
If for example property domains colorRGB, layer and sound are defined. Then
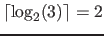 bits are needed to store the property vector type and the property
bits are needed to store the property vector type and the property layer has the value 01 .
The property vector type is followed by the elements of the property vector (see section 21.3.1 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) ). In which the number of elements and bits are determined by the respectively domain (see section 21.2.4 on page
). In which the number of elements and bits are determined by the respectively domain (see section 21.2.4 on page ![[*]](../pictures/crossref.png) ).
).
At the end the subobject of the property follows.
For the properties there are two special properties, that have influence on the decoding of the Fib object. These properties are "checksum" and "boundSize".




